Cholecystitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
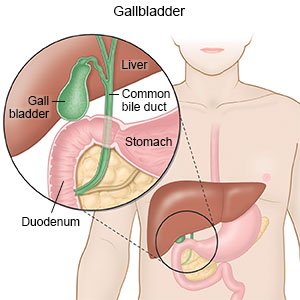
Cholecystitis is inflammation of your gallbladder. Your gallbladder stores bile, which helps break down the fat that you eat. Your gallbladder becomes inflamed if it is not able to release bile. You may have a sudden, severe symptoms (acute cholecystitis) or mild symptoms over a period of time (chronic cholecystitis).
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat an infection caused by bacteria.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Antinausea medicine may be given if you have nausea or are vomiting.
Tests:
- An ultrasound or CT may show one or more gallstones. You may be given contrast liquid to help the gallbladder show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan shows if your gallbladder is working. A radioactive liquid, called a tracer, will be injected into your vein. Your healthcare provider will be able to see if the tracer goes through your biliary tract or stays in your gallbladder.
Treatment:
- Cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your gallbladder.
- Cholecystostomy is a procedure to drain your gallbladder. A hollow needle will be put into your gallbladder through your abdomen. The bile in your gallbladder will be drained through this needle. You may also have a tube inserted in your gallbladder to drain it over several days or weeks.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
IV fluids
treat dehydration and help increase your blood pressure.
RISKS:
Cholecystitis may cause liver damage. You may develop an abscess (a buildup of pus) in your abdomen. You may develop a serious blood infection if cholecystitis goes untreated.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Cholecystitis
Treatment options
- Medications for Acute Cholecystitis
- Medications for Cholecystitis
- Medications for Gallbladder Disease
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
