Pressure Injury
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
A pressure injury is an injury to the skin and tissue under the skin. A pressure injury is also called a pressure sore, bedsore, wound, or decubitus ulcer. Pressure injuries can form over any area but are most common on the back, buttocks, hips, and heels. Pressure injuries can also happen in your mouth.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your doctor or specialist if:
- You have a fever.
- You have green or yellow drainage or a bad smell coming from your pressure injury.
- An area of your skin is very red and firm.
- You have new pain, or pain that is getting worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to decrease pain or to help treat or prevent a bacterial infection. Ask how to take these medicines safely.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
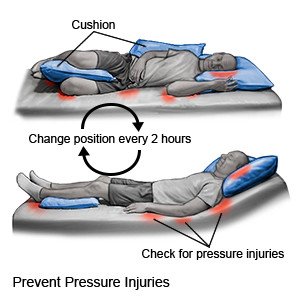
Change your position often:
Change your position every 2 hours if you are in a bed all day. Change your position every hour if you are in a wheelchair all day. Set an alarm to help remind you when it is time to turn. Keep a written turning schedule to help you remember to turn.
Care for your skin:
 |
- Clean and cover your injury. You may need to keep a bandage over your injury to protect the skin from more damage. You may also need to clean it with saline. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about when and how to change your bandages.
- Keep your skin clean, dry, and moisturized. Use mild soap and warm water to clean your skin. Do not rub or scrub when you wash. Do not use products that contain alcohol, because they can dry out your skin. Gently pat your skin dry. Do not rub your skin with a towel. Apply lotion or a moisturizer on your skin often.
- Protect your skin from tubes and medical devices, such as oxygen. Use a dressing to cushion the areas of skin where tubing or devices may be laid. Move the tubing or device and look at the skin every day. You may need to remove or move the tubing or device to another place.
- Protect the skin over bony areas. Use pillows or foam wedges to keep bony areas from touching, and to relieve pressure. For example, put a pillow or foam wedge between your knees to keep them from pressing on one another. Place a pillow or foam wedge under you to keep your hip raised when you lie on your side. Do not rest directly on your hipbone. Put a foam pad or pillow under your legs from calf to ankle when you lie on your back. The pad or pillow should raise your heels so that they are not touching the bed.
- Use specialty equipment, mattresses, or pads to decrease pressure. A draw sheet or large pad under you may help others move you up in bed. An overhead trapeze can help you change positions in bed. Mattresses and overlays made to provide more cushioning may help decrease the risk of pressure injuries. Examples include a foam mattress pad and air or water mattresses. Ask about equipment that may be right for you and how you use it.
Eat a variety of healthy foods:
Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, and fish. Foods that are high in protein may help your pressure injury heal. This includes lean meats, beans, milk, yogurt, and cheese. Nutrition shakes may also give you extra calories and protein if you have trouble eating or are underweight.
 |
Do not smoke:
Nicotine can damage your skin and slow healing. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need to return often so healthcare providers can check your injury. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
