Mastoiditis in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
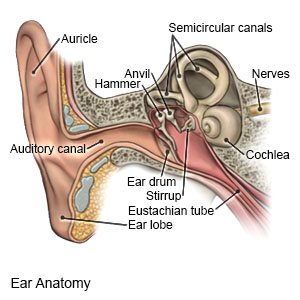
Mastoiditis is an infection in the air cells and mastoid bone of your child's skull. The mastoid bone is located behind your child's ear. Mastoiditis is most common in children younger than 2 years who have a history of ear infections. Mastoiditis is often caused by an ear infection that spreads. Your child's ear canal swells and traps fluid inside his or her ear. Trapped fluid causes bacteria to grow and spread to the mastoid bone.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that your child may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your child's medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done to your child. Make sure all of your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your child's vein that is used to give medicine or liquids.
Neurological signs,
also called neuro signs, neuro checks, or neuro status may be monitored. During a neuro check, healthcare providers see how your child's pupils react to light. They may check your child's memory and how easily your child wakes up. Your child's hand grasp and balance may also be tested. How your child responds to the neuro checks can tell healthcare providers if your child's illness or injury has affected his or her brain.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help fight or prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine for your child.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If your child takes blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for him or her. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Acetaminophen may be given to decrease your child's pain and fever.
Tests:
X-ray, CT, or MRI pictures may show bone damage, infection, or an abscess in your child's skull or brain. Your child may be given contrast liquid to help the pictures show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not let your child enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has any metal in or on his or her body.
Treatment:
- A myringotomy is surgery to help release pressure in your child's ear by making a small hole in his or her eardrum. Your child may also need tubes placed into his or her ear to relieve pressure and drain fluid. This may improve your child's hearing.
- A mastoidectomy is surgery to remove any infected part of your child's mastoid bone. Your child may need this surgery if his or her condition is severe, other treatments are not working, or your child has a fever. Your child may also need mastoidectomy if he or she has an abscess inside the mastoid bone.
- Drainage of an abscess in your child's ear, mastoid bone, or other areas in your child's skull may be needed. An abscess is an area that is swollen with fluid. Abscess drainage may be done if your child is not responsive, or has severe swelling in his or her brain.
RISKS:
Your child's mastoiditis infection may spread to other bones in his or her head, face, and neck. Your child's symptoms may come back, even after treatment. The infection may cause bone loss if it is not treated right away. Mastoiditis may cause permanent hearing loss. Mastoiditis may also result in a brain infection, seizures, facial nerve damage, brain swelling, or meningitis. Meningitis is swelling of the tissue (meninges) that surrounds your child's brain and spine. Mastoiditis may also cause blood clots in your child's sinuses.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Mastoiditis
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
