Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
What is hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)?
HUS occurs when a toxic substance is released into the bloodstream and destroys red blood cells. This causes bleeding, blood clots, and kidney damage. HUS is more common in young children than in adults.
What causes HUS?
Food that contains bacteria is the most common cause of HUS. An example is E. coli bacteria. The bacteria release harmful substances that injure blood vessels. The following can also cause HUS:
- Bone marrow transplant
- Cancer or chemotherapy
- Conditions that affect the immune system, such as lupus
- Infections such as influenza (flu) or HIV
- A type of hypertension (high blood pressure) that causes organ damage
- Certain medicines used to treat heart disease, clotting disorders, or diarrhea
- Pregnancy
What are the signs and symptoms of HUS?
- In children, irritability or changes in behavior
- Abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Bleeding from the lips, mouth, or nose
- Coughing and trouble breathing
- Little or no urine, or blood in the urine
- Fever
- High blood pressure
- Pale or blue skin, lips, or nails
- Pinpoint reddish spots, or purple bruises
- Fluid buildup in your lower legs and lungs
How is HUS diagnosed?
- Blood or urine tests may be used to check for signs of kidney damage or infection. You may also need to collect all of your urine for 24 hours for testing. This longer test gives more detailed information about your kidney function.
- A bowel movement sample is used to check for the germ that is causing your illness.
- A percutaneous kidney biopsy is a procedure to take a small piece of your kidney to be tested. Healthcare providers put a needle into your back and through to your kidney.
- Ultrasound pictures of your kidneys can show if you have kidney stones, an abscess, or other problems.
How is HUS treated?
- IV fluids help balance the fluid and salt in your body.
- Medicines such as anticonvulsants, steroids, and blood pressure medicine help control the symptoms of HUS.
- A blood transfusion is used to give whole or parts of blood through an IV.
- Dialysis cleans your blood when your kidneys cannot. Extra water, chemicals, and waste products are removed from your blood by a machine. Your blood is passed through a filter, then returned back into your body. You may need dialysis for a short time, or for the rest of your life.
- A plasma exchange is used to draw blood through an IV. A machine separates the plasma from your blood cells. Your plasma is then taken out and replaced with donor plasma or albumin. The blood cells, together with the replacement plasma or albumin, are then put back into your body through the IV.
- A kidney transplant may be needed if you have kidney failure.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What do I need to know about nutrition?
You may need to make changes to the foods you eat. Keep a list of foods you can eat. You may need to take vitamin and mineral supplements, such as calcium. Drink liquids as directed. You may need to write down how much liquid you drink and how much you urinate. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much of the following you can have each day:
- Limit protein to help your kidneys work better. Foods high in protein include beef, chicken, fish, eggs, and dairy products (milk, cheese, and yogurt).
- Limit the amount of phosphorus you have each day. Damaged kidneys cannot get rid of the extra phosphorus that builds up, leading to low calcium and bone fractures. Foods that are high in phosphorus are dairy products, beans, peas, and nuts. Phosphorous is also found in cocoa, beer, and soda.
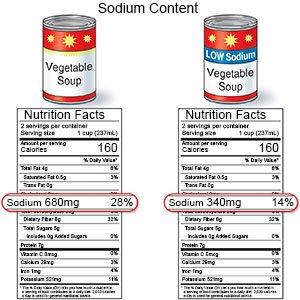
- You may need to limit the amount of sodium (salt) you eat each day. Sodium can lead to fluid buildup in your tissues and can damage your heart. Damaged kidneys cannot get rid of the extra fluid. Canned foods, processed meats such as sandwich meats and sausage, canned soups, and salted snacks are high in sodium.
- You may need to limit potassium. Potassium is found in foods such as fruits and vegetables. Your kidneys may not be able to get rid of extra potassium. This may cause potassium to build up in your blood. High potassium levels can lead to heart problems.
What can I do to prevent foodborne diseases?
Make sure everyone in your house follows these rules:
- Wash your hands often. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Use soap and water every time. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Wash the front and back of each hand, and in between your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available.

- Keep raw and cooked foods separate. Do not put cooked food on an unwashed cutting board, plate, or storage container that had raw food on it. Store raw and cooked foods separately in the refrigerator.
- Keep food surfaces and utensils clean. Clean surfaces before and after you prepare food. Use paper towels you can throw away or cloths you can wash between uses. Wash cutting boards and utensils after each use and before you prepare the next food.
- Wash fruits and vegetables before you eat or cook them. Use a vegetable brush to scrub firm items such as carrots and potatoes. Wash leafy greens such as lettuce. Pull heads of lettuce apart to wash inner leaves.
- Cook food thoroughly. Food is safely cooked when it reaches a temperature high enough to kill bacteria. Ask healthcare providers for more information on cooking food safely.
- Store food in the refrigerator. Put leftover food in the refrigerator as soon as possible. This can prevent food from spoiling and causing illness.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are urinating less than usual or not at all.
- You have diarrhea and are vomiting.
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You have a severe headache, trouble thinking, and are confused.
- You have trouble seeing.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You have bleeding from your gums, lips, or nose.
- You have bloody or dark urine or bowel movements.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
