Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
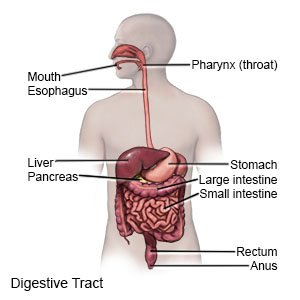
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding may occur in any part of your digestive tract. This includes your esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, or anus. Bleeding may be mild to severe. Your bleeding may begin suddenly, or start slowly and last for a longer period of time. Bleeding that lasts for a longer period of time is called chronic GI bleeding.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Your symptoms return.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You have heartburn.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Activity:
Rest as directed. Ask when you can return to your usual activities, such as work. Slowly do more each day.
Nutrition:
Ask if you need to be on a special diet. A special diet can help treat GI conditions and prevent problems such as GI bleeding. Eat small meals more often while your digestive system heals. Avoid or limit caffeine and spicy foods. Also avoid foods that cause heartburn, nausea, or diarrhea.
Prevent GI bleeding:
- Manage GI conditions as directed. Examples of GI conditions include gastroesophageal reflux, peptic ulcer disease, and ulcerative colitis. Take all medicines for these conditions as directed.
- Limit or do not take NSAIDs. Ask your healthcare provider if it is safe for you to take NSAIDs. NSAIDs can increase your risk for ulcers and GI bleeding.
- Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can cause ulcers and esophageal varices. Esophageal varices are swollen blood vessels in your esophagus. Over time the blood vessels become weak and may bleed.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can increase your risk for ulcers. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need to return for a colonoscopy, endoscopy, or other tests. These tests can make sure you do not have more bleeding. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
