Nonruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
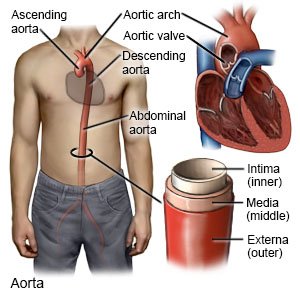
An AAA is a bulging or weak area in your abdominal aorta. Over time, the bulge may grow and is at risk for tearing or rupturing (bursting). The aorta is a large blood vessel that extends from your heart to your abdomen. The part of the aorta that extends into your abdomen is called your abdominal aorta. Your abdominal aorta brings blood to your stomach, pelvis, and legs. Treatment may be needed so your aneurysm does not grow and rupture. An AAA rupture is a life-threatening emergency.
 |
What increases my risk for an AAA?
- Use of nicotine products or drugs such as cocaine
- High blood pressure (BP) or atherosclerosis (the buildup of fat and cholesterol in your arteries)
- Extra body weight
- A family or personal history of an AAA
- Being male or older than 65
- An abdominal injury
- A connective tissue disorder such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome
What are the signs and symptoms of an AAA?
An AAA usually does not have signs or symptoms if it has not ruptured. You may have any of the following if the AAA leaks or ruptures:
- Sudden pain in your abdomen, groin, back, legs, or buttocks
- A lump or swelling in your abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff abdominal muscles
- Numbness or tingling in your legs
- Pale, sweaty, or clammy skin
- Dizziness, fainting, or loss of consciousness
How is a nonruptured AAA diagnosed?
An AAA may be found when you have a test done for another condition. Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your medical history. Tell the provider if you have any symptoms and when they started. Tell your provider about any medicines you take. You may be given contrast liquid before some of the following tests. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- An ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may show the aneurysm or a condition causing it. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Angiography may be used to take detailed pictures of the AAA and your blood vessels.
How is an AAA treated?
Your AAA may not need treatment. Your healthcare provider may monitor the size of your AAA with tests, such as an ultrasound. If your AAA gets bigger, starts to leak, or ruptures, you may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be needed to lower your BP or cholesterol level.
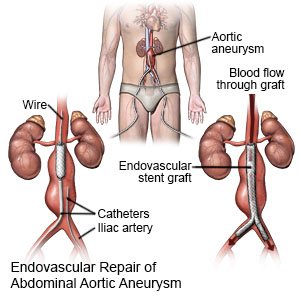
- Endovascular repair is a procedure that uses a graft to repair your AAA. The graft stops blood flow to the aneurysm and protects your abdominal aorta. You may need to have more than 1 endovascular repair.
- Open repair is surgery to repair or remove an AAA.
 |
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage a nonruptured AAA?
- Do not use nicotine products or stimulating drugs. Nicotine and drugs such as cocaine may raise your BP, damage your aorta, and make your AAA larger. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke or use stimulating drugs and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Do not use these in place of cigarettes. Avoid secondhand smoke.
- Manage other health conditions that can cause or worsen an AAA. Follow your treatment plan to manage conditions such as high cholesterol, obesity, or stress. Check your BP as directed if you have high BP. Your provider will show you how to do this. Check your BP 2 times, 1 minute apart. Check as often as directed each day. Keep a record of your readings and bring it to your follow-up visits.

- Follow physical activity directions. Your healthcare provider may help you create a physical activity plan. Your plan may include low-intensity activity, such as walking, yoga, or swimming. Do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds. You may also need to avoid intense physical activity, such as running. Heavy lifting or intense activity may raise your BP or put pressure on your aorta. These increase your risk for a tear or rupture.

- Follow the meal plan recommended by your provider. Talk to your provider or dietitian about a heart-healthy or low-sodium meal plan. A meal plan may help you lower your cholesterol or BP levels. Heart-healthy meal plans are low in sodium, processed sugar, and some fats. They are high in potassium, calcium, heart-healthy fats, and fiber. These can be found in vegetables, fruit, and whole-grain foods.
- Know the risks if you choose to drink alcohol. Alcohol can increase your BP. Ask your provider if it is okay for you to drink any alcohol. Your provider can help you set limits for the number of drinks you have in 24 hours and within 1 week. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
- Get vaccines as directed. Some viruses can worsen an AAA. Get an influenza (flu) vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October. Get all recommended COVID-19 vaccine doses and boosters. A pneumonia vaccine may also be recommended. Your provider will tell you if you need other vaccines, and when to get them.
What do I need to know about family planning?
- Before you try to get pregnant, talk to your specialist about family planning. Genetic counseling may be needed if your AAA is caused by a condition that can be passed to your baby. You may need counseling if your condition can put you or your pregnancy at risk. You may instead need counseling about the risk of pregnancy making your AAA grow, tear, or rupture. You may also need tests to check your AAA. These tests can help you and your provider plan treatment before and during your pregnancy. You may need surgery to protect your aorta and prevent your AAA from growing, tearing, or rupturing.
- While you are pregnant, you may have 1 or more specialist caring for you. You may need medicine to help lower your BP. You may need regular tests to check your AAA. You may need other medicines or surgery if your AAA grows, tears, or ruptures. Your baby may need to be born early if your aorta tears or ruptures. A cesarean section (C-section) may be needed if you have a history of a tear in your aorta. You may need a C-section if you have a high risk for a ruptured aneurysm or tear.
- After your baby is born, you may need tests to check your AAA. Your risk for a ruptured aneurysm or tear is high for up to 12 weeks.
What do I need to know about screening for an AAA?
Your healthcare provider can give you specific information about your screening. The following is general information:
- Screening means you are checked for an AAA even if you have no signs or symptoms. Screening is recommended if you are male, aged 65 to 75 years, and you ever smoked cigarettes. Screening may be recommended based on your family history and other personal risk factors.
- Your parents, siblings, and children may need screening. More family members may also need screening if 2 or more people in your family had an AAA. Your provider will tell you which family members need screening.
- The benefit of screening is that your provider can diagnose an AAA early. This helps your provider monitor your AAA and start treatment, if needed. This can help prevent your AAA from growing, rupturing, or tearing. Screening can also help you plan a healthy pregnancy.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone else call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
-

- You faint or lose consciousness.
- You cannot be woken.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have sudden sharp pain in your abdomen, groin, back, legs, or buttocks.
- You have nausea and are vomiting.
- You feel dizzy.
- You have stiffness or swelling in your abdomen, or a lump in your abdomen.
- You have numbness or tingling in your legs.
- Your skin is pale, sweaty, or clammy.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Nonruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
