Heart Attack
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
What is a heart attack?
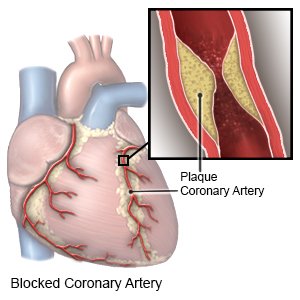
A heart attack happens when the blood vessels that supply blood to your heart are blocked. This can damage your heart or lead to an abnormal heart rhythm or heart failure. A heart attack is also called a myocardial infarction.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a heart attack?
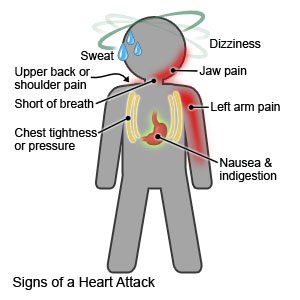 |
- Chest pain, tightness, or heaviness that can last 30 minutes or longer
- Pressure, crushing, squeezing, or burning in your chest
- Discomfort that spreads to your neck, jaw, shoulders, back, or arms
- Heartburn, abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Feeling weak, dizzy, or like you are going to faint
- Trouble catching your breath or taking a deep breath
- Feeling cold and sweaty
- Fast heartbeat
- You may not have typical symptoms if you are a woman or an older adult, or have diabetes or heart failure. You may only have shortness of breath and no other symptoms. You may have no symptoms at all.
What is the difference between angina and a heart attack?
Angina is chest pain, tightness, or discomfort that comes and goes. It gets worse with activity or stress. It gets better with rest, medicine called nitroglycerin, or both. Angina does not damage the heart like a heart attack does. Angina may be a warning sign that you are at risk for a heart attack. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on angina.
What causes a heart attack?
- Plaque , also called fatty deposits, can build up inside one or more of your coronary arteries. This can cause the arteries to become narrow and slow or block the blood flow. Small pieces can also break off and block blood flow.
- Blood clots may form on each side of the plaque. This can slow or stop blood flow to your heart.
- Heart spasm is when a coronary artery suddenly tightens and stops blood flow to part of the heart.
What increases my risk for a heart attack?
- High cholesterol, diabetes, or high blood pressure
- Smoking cigarettes or chewing tobacco
- A family history of heart attack
- Being a man older than 55
- Being a woman who has gone through menopause
- Use of illegal drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamines
- Obesity or being overweight for several years
- A lack of physical activity, especially sitting for long periods every day
How is a heart attack diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask when your chest pain started, what it feels like. Tell the provider if anything makes the pain better or worse. He or she will ask if you took nitroglycerin or other medicines. He or she will ask you about your medical history and if you have had these signs and symptoms before. You may need the following tests:
- Blood tests can help healthcare providers know if your heart has been damaged.
- X-ray pictures may show an enlarged heart or fluid in your lungs.
- An EKG records your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats. It is used to check for damage to your heart.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure and function of your heart.
- Angiography is a test used to look for blockage in your coronary arteries, such as plaque or blood clots. A thin tube called a catheter is placed into an artery, usually in your groin. Contrast liquid is put through the catheter, and x-ray pictures are taken of the blood flow. Tell healthcare providers if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
How is a heart attack treated?
- Medicines may be given to help the coronary arteries open so your heart can get the blood it needs. Medicine may also help decrease pain, blood pressure, or control your heart rate. You may also need medicine to help thin your blood to keep clots from forming. This medicine makes it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. After a heart attack, you may also be given medicine to decrease the amount of cholesterol and plaque in your blood.
- Do not take certain medicines without asking your healthcare provider first. These include NSAIDs, herbal or vitamin supplements, or hormones (estrogen or progestin).
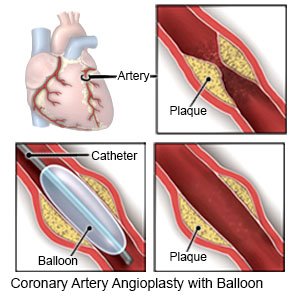
- Angioplasty is a procedure to open an artery blocked by plaque. A small tube with a balloon on the end is threaded into the blocked artery. After the tube is in the artery, the balloon is filled with liquid. As the balloon fills, it presses the plaque against the artery wall so blood can flow through the artery more easily.
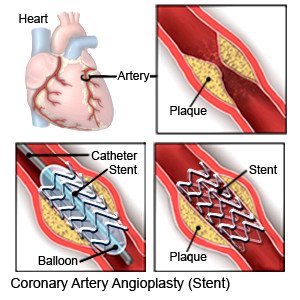
- Coronary intravascular stent placement is also called coronary artery stenting. The stent is a small mesh wire that is inserted into an artery to keep it open so blood can flow through it.
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is also known as heart bypass surgery or open heart surgery. CABG can improve blood flow to the heart by sending blood around a blocked part of an artery. This surgery may also decrease your risk for a heart attack in the future.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What should I do if I think I am having a heart attack?
If you have chest pain for 2 to 3 minutes, stop what you are doing. Call 911 if your chest pain does not go away or gets worse within 5 minutes. Sit or lie down while you wait for the ambulance.
What can I do to manage my health?
- Check your blood pressure at home. High blood pressure can lead to a heart attack. Sit and rest for 5 minutes before you take your blood pressure. Extend your arm and support it on a flat surface. Your arm should be at the same level as your heart. Follow the directions that came with your monitor. If possible, take at least 2 readings each time. Take your blood pressure at least 2 times each day at the same times, such as mornings and evenings. Keep a record of your readings and bring it to your follow-up visits. Ask your healthcare provider what your blood pressure should be.

- Get a flu vaccine every year as soon as it is available. The vaccine will help prevent the flu. A heart attack will make it harder for you to fight off the flu virus on your own. The flu may also be worse for you than for a person who has not had a heart attack. Ask about other vaccinations you may need.
What lifestyle changes may I need to make after a heart attack?
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung and heart damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Follow a heart-healthy diet. A heart-healthy diet is an eating plan low in total fat, unhealthy fats, and sodium (salt). A heart-healthy diet helps decrease your risk for heart disease and stroke. Limit the amount of fat you eat to 25% to 35% of your total daily calories. Your healthcare provider may recommend the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Eating Plan to help lower high blood pressure and LDL (bad) cholesterol. The plan is low in sodium, sugar, unhealthy fats, and total fat. It is high in potassium, calcium, magnesium, and fiber. Ask for more information about this plan.
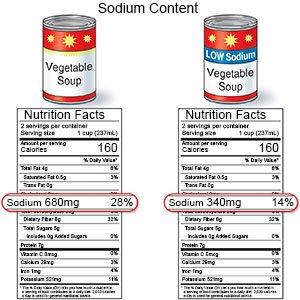
- Limit sodium (salt) as directed. Too much sodium can affect your fluid balance. Check labels to find low-sodium or no-salt-added foods. Some low-sodium foods use potassium salts for flavor. Too much potassium can also cause health problems. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much sodium and potassium are safe for you to have in a day. He or she may recommend that you limit sodium to 2,300 mg a day.
- Exercise as directed. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you. Exercise makes your heart stronger, lowers blood pressure, and helps prevent a heart attack. The goal is 30 to 60 minutes a day, 5 to 7 days a week. You may have to work up to this goal. Healthcare providers can help you reach this goal, starting in cardiac rehab sessions.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider how much you should weigh. He or she can help you create a safe weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Manage stress. Stress may increase your risk for a heart attack. Learn ways to control stress, such as relaxation, deep breathing, and music. Talk to someone about things that upset you.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are tired and cannot think clearly.
- Your heart is beating faster than usual.
- You are bleeding from your gums or nose.
- You see blood in your urine or bowel movements.
- You urinate less than usual or not at all.
- You have new or increased swelling in your feet or ankles.
When should I call my doctor or cardiologist?
- You have trouble taking your heart medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Heart Attack
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
